Impact of Striking Down Race-Based Admissions by the US Supreme Court on International Students
Affirmative Action is a direct result of the Civil Rights movement of the 1960s, which brought questions of equity and justice to the forefront of the US national discourse. It entailed the government crafting policies to help minorities and marginalized groups gain more access to opportunities, especially in Government, that have historically been denied to these groups. Affirmative Action is targeted toward providing opportunities to underrepresented communities based on gender, race, religion, and national origin. In 1965, President Lyndon Johnson issued an executive order requiring all government contractors and subcontractors to expand job opportunities to minorities. In his historic address at Howard University, President Johnson said, “You do not take a person who, for years, has been hobbled by chains and liberate him, bring him up to the starting line of the race and then say, ‘you are free to compete with all the others,’ and still justly believe that you have been completely fair.” Since then, Affirmative Action has been a cornerstone of University admissions in the US.
On June 29, 2023, the US Supreme Court declared that the race-conscious affirmative action programs at Harvard University and the University of North Carolina are unconstitutional and violate the Constitutional Guarantee of Equal Protection, effectively ending race-conscious admission decisions across the US. No longer will the race of a student be considered a parameter for Admission to a University.
What Does the Judgment Mean for University Admissions?
To answer this question effectively, we need to examine what happened after Proposition 209 was implemented in California in November 1996. Proposition 209 ended all forms of affirmative action policies in admission decisions. According to a 2020 study, reported by NPR, the Black and Hispanic population in selective institutions at UCLA and UC Berkeley fell by over 40%. The Black and Latino students, because of the ban, applied to less competitive colleges. Although California was the first state to ban affirmative action in college admissions, by 2021 affirmative action was banned in 8 other states. Another study conducted by The Washington Post on 30 years of race and ethnicity data from the nine states that have banned affirmative action found that Whites and Asian Americans are overrepresented in public schools in the states that have banned it, while multiracial students and Latinos are underrepresented.
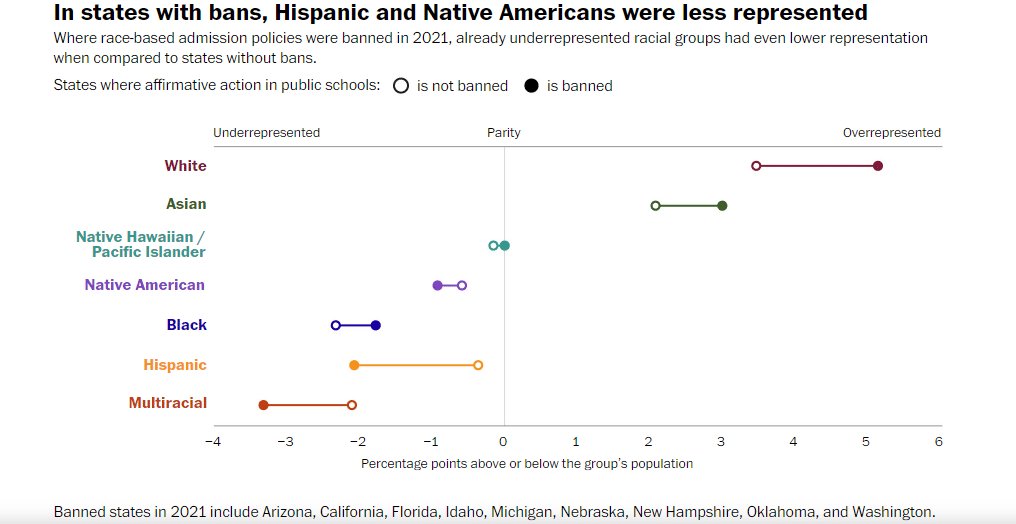
However, the above infographic does not tell the entire story as it considers all public schools in the state and not just top schools with low acceptance rates. According to a report published in Time Magazine, “The average gap between Black and White student graduation rates at the top dozen public universities without affirmative action was 10.1% in 2020, as found by the University of California Los Angeles. In contrast, the gap was 6% at the top dozen public universities that utilized affirmative action.” It’s important to note here that the churn, because of this Supreme Court decision, is most likely to be seen at top and selective schools in the USA. The admission protocols of less competitive schools are likely to remain the same. A study conducted by Pew Research found that in 2017 more than 50% of US schools accepted a staggeringly high 70-100% of all students who apply to these schools.
Clearly, race has been a significant determining factor in University Admissions, and its removal from the criteria for selecting students would necessitate a major overhaul in the admission policy for most top schools. Most top schools are determined to maintain a diverse student pool. Apprehending that such a decision might come from the US Supreme Court, several of these Universities have already put policies in place to retain the diversity of their campus. This determination to keep the University campus diverse will undoubtedly have a positive impact on International Students applying to the US, especially from countries with fewer students studying in the US.
Affect on International Students
Enhanced Importance of the Essay: It is important to note that even though the US Supreme Court has struck down race-based admissions, the Chief Justice noted the following: “Nothing in this opinion should be construed as prohibiting universities from considering an applicant’s discussion of how race affected his or her life, whether through discrimination, inspiration, or other means,” and that these challenges could be put across by a student in his or her Personal Essay. This will significantly elevate the importance of essays in the admission process to top universities. Accordingly, Harvard University has already modified its essay requirements. The Executive Director of the College Excellence Program at The Aspen Institute wrote in an email: “The changes Harvard made to its application are clearly designed to help admissions do what the Supreme Court said is acceptable – namely, to consider race as part of an applicant’s experiences as an individual – not based on race.” This will also help International Students, many of whom already come from a different culture, by giving them more space to put across their personal and social struggles.
Reduced Importance of Standardized Tests: The importance of standardized tests might diminish further, as they harm campus diversity. There’s no doubt that for top schools, a student’s academic credentials remain the most crucial factor in admissions. However, several studies have demonstrated that higher GPAs and elevated scores on standardized tests are positively correlated with the economic prosperity of a student’s family. The better access a student has during primary and secondary education, the greater the likelihood of achieving high scores on these tests. Although individuals with high standardized scores will have a substantial edge in being accepted to selective schools, more institutions might adopt a Test Optional policy in the future to enhance campus diversity.
Legacy Admissions: Certain universities might decrease the importance of legacy admissions, a practice by which a student is admitted based on their connection to an alumnus/alumna. If legacy admissions are reduced or, better still, completely eliminated in some of the top schools to enhance campus diversity, international students could potentially reap the advantages of such changes.
National Origin: Although race-based Affirmative Action has been invalidated by the Supreme Court, Affirmative Action that extends beyond race remains legally permissible. As universities endeavor to enhance campus diversity through alternative means, a student’s national origin could emerge as a pivotal factor in maintaining the diversity of a University campus. If this indeed becomes the case, the likelihood of an international student being admitted to a university may increase. This could potentially represent the most favorable outcome for an international student. However, it is important to note that countries with lower representation in US higher education would stand to gain considerably more compared to countries already having a substantial student presence.
References:
- https://www.livelaw.in/amp/top-stories/race-based-affirmative-action-in-college-admissions-unconstitutional-us-supreme-court-231542#amp_ct=1691643418406&_tf=From%20%251%24s&aoh=16916433007921&referrer=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.google.com
- https://time.com/6291497/affirmative-action-college-admissions-process/
- https://www.urban.org/urban-wire/future-college-admissions-without-affirmative-action
- https://www.chronicle.com/article/u-s-supreme-court-strikes-down-race-conscious-admissions-nationwide
- https://nyunews.com/news/2023/07/03/nyu-supreme-court-affirmative-action-ruling/#:~:text=Throughout%20both%20cases%2C%20NYU%20has,affirmative%20action%20in%20admissions%20decisions.
- https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2019/04/09/a-majority-of-u-s-colleges-admit-most-students-who-apply/
- https://www.washingtonpost.com/education/2023/06/29/affirmative-action-banned-what-happens/
- https://www.npr.org/2023/06/30/1185226895/heres-what-happened-when-affirmative-action-ended-at-california-public-colleges
- https://cshe.berkeley.edu/publications/affirmative-action-mismatch-and-economic-mobility-after-california%E2%80%99s-proposition-209
- https://www.nytimes.com/2020/08/21/upshot/00up-affirmative-action-california-study.html
- https://www.axios.com/local/san-francisco/2023/07/03/affirmative-action-supreme-court-california
- https://www.thecrimson.com/article/2023/8/3/harvard-admission-essay-change/
